A good profit margin falls between 5% and 10%, according to Brex, a financial services company. That said, good profit margins vary widely by industry, with some sectors, such as alcohol and food service, netting comparatively high margins.
However, coming up with a target profit margin is a highly personalized process that must account for your business’s various characteristics and operating costs. Let’s go through the process to determine what a good profit margin is and explore small business profit margins by industry.
What Is Profit Margin?
Your profit margin is what you earn in relation to your overall revenue. There are a few types of profit margins small businesses consider:
- Gross profit margin: Your gross profit margin is the amount of money you retain from product sales after subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS).
- Operating profit margin: This measures how well a company can turn revenue into profit after accounting for the business costs, including COGS and operating expenses, such as rent, payroll and marketing.
- Net profit margin: This is the ratio of net income (i.e., income after expenses, depreciation, etc.) relative to revenue.
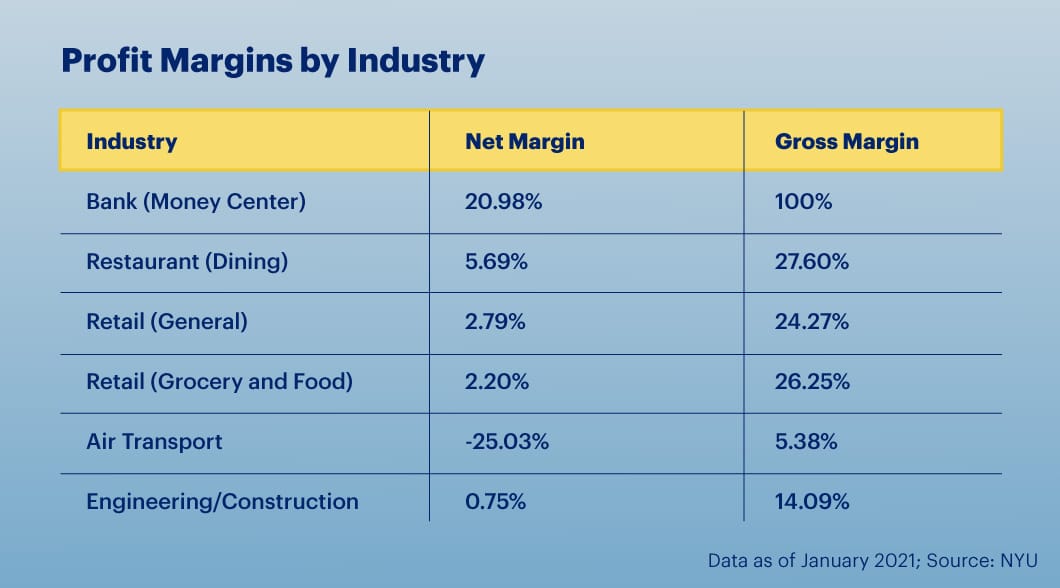
Average Profit Margin by Industry
The average profit margin across all industries is 7.71%, according to a study by New York University.
However, no two profit margins will ever perfectly resemble each other at any time. What’s considered a good profit margin and an average profit margin for a small business depends on your industry, long-term growth goals and the overall state of the economy.
Industries With Lower Profit Margins
Hovering in the 2% range, lower profit margins are common in the grocery store, automobile dealership, lawn care and beverage manufacturing industries.
Industries With Higher Profit Margins
On the other end of the spectrum are industries such as dental care, car rental services and tax and accounting services, which consistently run net margins of more than 20%.
What Factors Can Impact a Good Small Business Profit Margin?
Various components can affect what’s considered a good profit margin. Here are some of the factors to consider.
Industry
As mentioned, industry is a major contributing factor in what’s considered a good profit margin for a small business. In some industries, the average small business profit margin hovers around 2%, while other industries have quarters that exceed even 34%.
Additionally, variations in the number of employees, skill levels, tax rates and scale all play into the average profit margin for your small business that you’ll pull in quarter after quarter.
Other industry-related variables that can affect the profit margin of small business include:
- Labor costs
- Use of assets
- Equipment maintenance
- Inventory management
- Cost control systems
- Physical location
- Regulatory environment
Expansion
Expansion is another top variable that influences a company’s profit margin, so consider your growth goals for your business when arriving at a target average profit margin.
If you’re satisfied with your business’s current revenue, you don’t have to ramp up expenses or reinvest profits. However, for those who want a larger slice of the pie, aiming above 20% profit margins can make the difference between withstanding downward market fluctuations.
Scale
Account for scale when determining what is a reasonable profit margin for your small business. For example, startups with few or no employees have fewer expenses and are more likely to generate higher margins.
By contrast, megacorporations with rent, payroll and employee benefits, such as Ford, Target and Walmart, tend to have single-digit margins.
Also, overhead costs can make a big difference between a high and an average profit-generating business.
For example, independent consultants have virtually no overhead costs compared to a restaurant or nightclub owner who has to cover rent, payroll and inventory, among other recurring expenses.
Economic Changes
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly disrupted the economic sector, causing even relatively stable average profit margins by industry to change in 2020 and 2021, according to Camino Financial. It could take years before gross and net profit margins return to pre-pandemic averages.
Inflation is another economic factor that can significantly affect profit margins. Recently, inflation has reached records not seen since the early 1980s. Without a doubt, rising costs of raw goods, rent, fuel and labor impact how much a business can net, even if the business successfully increases its prices.
How Do You Calculate Profit Margin?
Similar to calculating your company’s operating cash flow (OCF), calculating profit margins involves a bit of simple division. Keep track of every expense so you can accurately figure your sunk costs (down to maintenance and transaction fees).
Although accounting tools are available to help you find your margins, you can also quickly calculate them yourself using pen and paper.
Gross Profit Margin
To find your gross profit margin, take the net sales, or revenue, and subtract the cost of labor and materials (COGS). Then, when you have that figure, divide it by the revenue to find the gross profit margin, multiplying by 100 to convert it to a percentage.
Gross Profit Margin = [(Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue] x 100
For example, consider a business with $2 million in revenue and $500,000 in COGS. This business would have a net margin of 75%.
Gross Profit Margin Example = [(2,000,000 – 500,000) / 2,000,000] x 100 = 75%
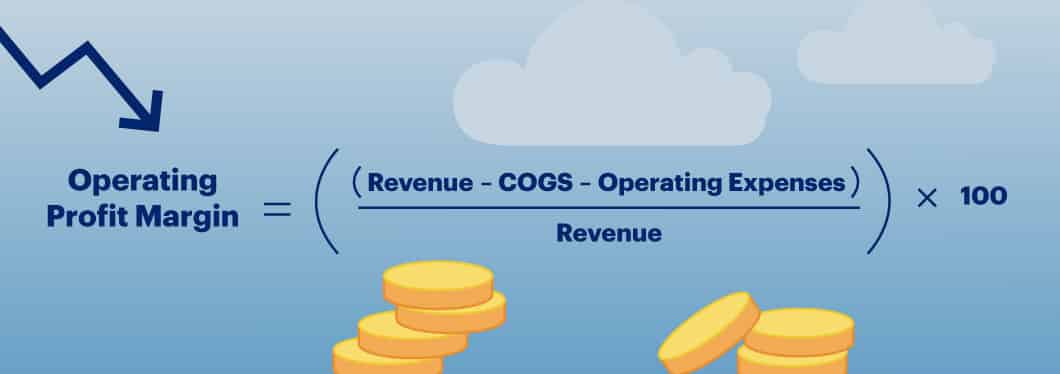
Operating Profit Margin
To calculate the operating profit margin, take the revenue and subtract the COGS and all operating expenses. Then divide that by the revenue and multiply by 100 to calculate your profit margin percentage.
Operating Profit Margin = [(Revenue – COGS – Operating Expenses) / Revenue ] x 100
Again, let’s assume $2,000,000 in revenue, $500,000 in COGS and $350,000 in operating expenses.
Operating Profit Margin = [2,000,000 – 500,000 – $350,000) / 2,000,000] x 100 = 58%
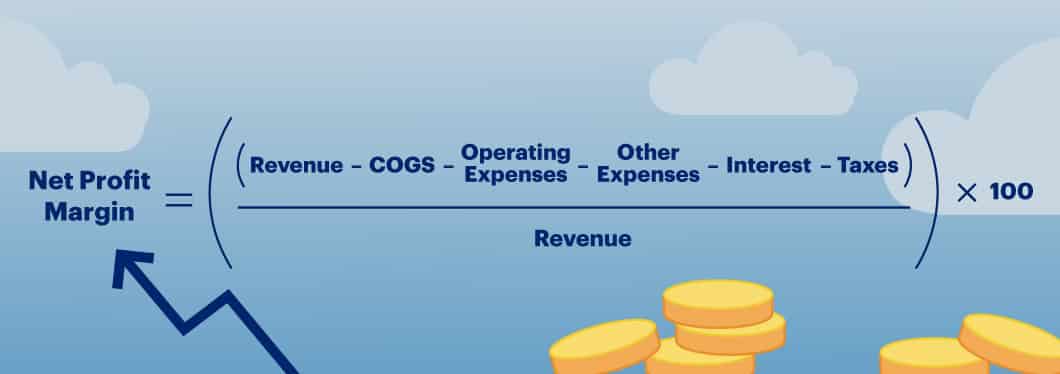
Net Profit Margin
To find your net profit margin, which is used to determine the company’s overall profit margin, you need to subtract all expenses from revenues. Then, divide that sum by total revenues to find your net profit margin.
Net Profit Margin = [(Revenue – COGS – Operating expenses – Other expenses – Interest – Taxes) / Revenue] x 100
For a net profit margin example, consider the business with $2 million in sales and $1 million in total expenses, including $500,000 in COGS, $350,000 in operating expenses, $50,000 in interest and $100,000 in taxes. This business would have a net margin of 50%.
Net Profit Margin Example = [(2,000,000 – 500,000 – 350,000 – 50,000 – 100,000) / $2,000,000) x 100 = 50%
Keep in mind that net margin, also referred to as net profit ratio, is always lower than the gross profit ratio and operating profit ratio. As such, it is the best representation of your company’s financial health and overall efficiency because it considers all the overhead costs that went into the sale of a good or service.
Note that net profit ratios are only a portion of your company’s financial story. For example, heavy capital investment, research and development expenses and marketing expenses can drive down your net profit ratios even though they’re solid indicators of long-term growth.
Don’t be tempted to buff up your net profit percentage by delaying certain discretionary expenses.
Tips for Improving Your Profit Margin
Cut Expenses
Asking “what is a good net profit margin” often shrouds the judgment of small business owners. Instead, a good profit margin can usually be generated by simply reducing overhead expenses wherever possible.
Fine-Tune Product Mix
Once you determine what is a good profit margin for a product or service within your small business, eliminate all those that fail to make the cut. For instance, if you sell coffee at 50% margins but pastries at 5%, your pastry inventory may need to be cut back.
Pad Inventory
One of the most effective ways to ensure your small business has a good profit margin is to plan your inventory wisely. Take the time to research your market so you can meet product demand without overstocking or suffering a shortage. It’s generally a good idea to overestimate the supply of whichever products generate the highest product margin.