Cybersecurity is a big deal. While business owners are aware of the risks, they may not know how to combat them. What they need are some small business cybersecurity tips.
Large companies have cybersecurity teams and budgets that protect their data against common threats such as ransomware, phishing attacks and other cyberattacks. But smaller businesses may not be able to afford or have the time to build a cybersecurity team or hire an outside firm.
With that in mind, let’s learn more about these threats and how small businesses can combat them.
Why Do Small Businesses Need Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is a necessary component in every business, no matter the size. It provides security measures that combat online threats to steal or wreak havoc with its data.
According to Verizon’s 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report, the top reason for breaches is financial motivation at 86%, followed by espionage at 10%.
Whether these reasons are fair is beyond the point. The assumption is there will always be someone who will try and ruin your business. Therefore, the goal of cybersecurity is to keep the riff-raff away from your pertinent business and user data.
Setting up a dependable security system allows people in the organization to focus on the job at hand without looking behind their backs for potential threats looming their way.
Why Are Small Businesses Vulnerable to Cyberattacks?
The biggest issue with cybersecurity among small businesses is how most fail to implement the practices across the board. BullGuard reports that 43% of small businesses don’t have cybersecurity in place. That means they are running the risk of getting hacked without having contingencies to protect their and their users’ information.
This reason is indicative as to why small businesses are prone to cyberattacks. Not only do they ignore security measures, whether deliberate or not, but some think they can recover from a security breach after it happens.
About 92% of small business executives “said they believe their businesses are prepared to recover from a disaster,” according to a survey by Infrascale. The problem here is that more than 20% of the same respondents don’t have a disaster recovery solution and data backup they can use if a cyberattack happens.

Common Cybersecurity Threats for Small Businesses
In Accenture’s ninth annual “Cost of Cybercrime” study in 2019, security breaches have increased by 11% since 2018 and 67% since 2014.
Worse, cyberattacks reached a record high in 2020. The pandemic didn’t stop hackers from exposing more than 36 billion records by the end of September 2020, according to Risk Based Security.
Again, these data point to why small businesses need to set up cybersecurity and protect themselves from these malicious attacks. To help aid them in finding the right solutions for their organization, they must find the most common online threats that their businesses have to deal with regularly.
Here are a few of the most infamous online threats every business must watch out for:
Phishing
Phishing refers to the act of sending emails or messages that are disguised as legitimate messages, but actually are attempts to steal information such as usernames, passwords and credit card numbers.
For example, a small business may receive a phishing email from a customer asking for their account information. The small business could inadvertently share this information with someone posing as a satisfied customer.
A small business should avoid giving out any personal or financial data over email or an instant message if they aren’t 100% sure of the person on the other end.
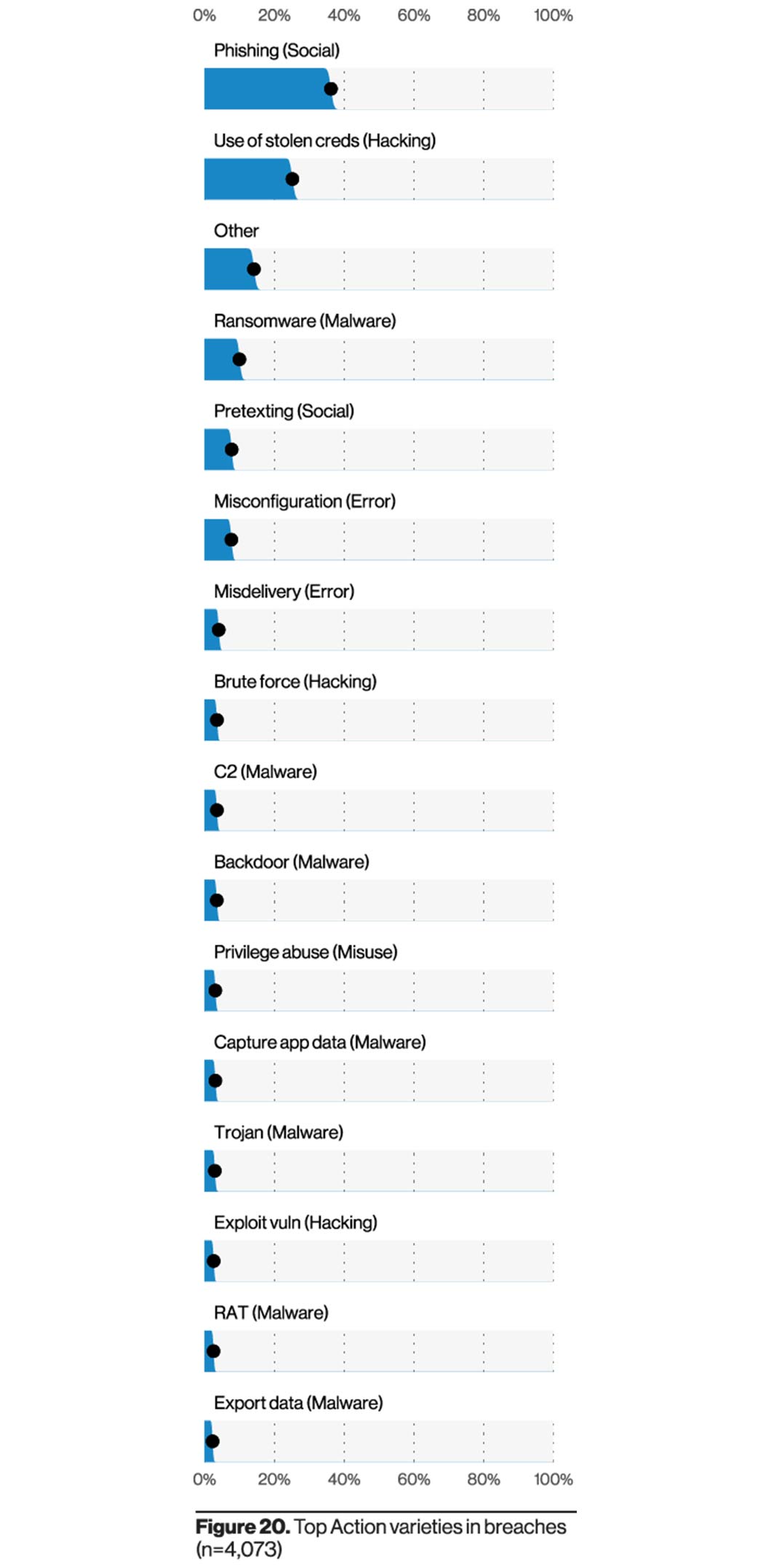
Thanks to its seemingly legitimate appearance, this type of online threat is the biggest problem among small businesses, with 36% affected businesses, according to Verizon’s 2021 Data Breach Investigations Report, 11% more than the previous year.
Watering Holes
Watering holes are an attack method that involves infecting the websites of small business partners and suppliers. Hackers wait to see which ones visit those sites and take advantage of any vulnerabilities.
The gains from a watering hole attack are small and companies use small businesses as a way to distribute malware-laden malvertising, resulting in small businesses unknowingly distributing malicious ads for the attack.
Drive-By Downloads
Drive-by downloads are when you get a message on the internet and it takes something bad along with it. It can take pictures, videos or any virus.
How Does a Cyberattack Impact a Small Business?
Consider that the average cost of a cyberattack for businesses with a headcount of less than 500 was $7.68 million, according to the ”2020 Cost of Insider Threats: Global” report sponsored in part by International Business Machines. It shouldn’t come as a surprise that the majority of businesses fold after an event like this.
Companies can pay a hefty price after a cyberattack. This includes informing parties affected by the breach (mainly customers and partners) and paying for insurance premiums. Most importantly, small businesses must deal with the backlash from their audience, especially its paying customers.
According to a study by DHM Research and ReputationUs, 46% of Oregonians blame the corporation when a cyberattack takes place. While 54% goes to the hacker, the high percentage also shows that businesses must be accountable for anything that happens with the sensitive data entrusted to them, whether they like it or not.
To be clear, the results of this small sample size isn’t indicative of the belief that the larger consensus holds. However, it can’t be denied that small businesses aren’t innocent bystanders when an online attack happens. They have to be held responsible to some degree because people put their trust in these businesses to take care of their personal data.
Because of the trust that was lost due to the online attack, expect lost revenues to follow.
A poll conducted by Javelin Strategy & Research involving more than 5,000 respondents shows that 33% of consumers were unwilling to do business with a corporation where a data breach took place.
6 Small Business Cybersecurity Tips
As a small business owner, you should make cybersecurity a top priority in your organization. By having the right system in place, you can have peace of mind and proceed with operations smoothly.
To help you get started, below are small business cybersecurity tips that you can immediately implement.
1. Hold Your Employees Accountable
Compile a clear list of guidelines to promote the safe use of social media sites for employees. Re-examine company policy on how sensitive information can be shared with people outside the company.
Keeping employees up to speed with the latest security protocols helps keep a business safe from online threats. However, what if the threat is from the inside?
I’m referring to employee negligence, the biggest risk to U.S. cybersecurity. Some 47% of business leaders said “human error such as accidental loss of a device or document by an employee had caused” a data breach, according to an industry report by information security company Shred-it. Even if it was an accident or innocent mistake by an employee, there’s no going back after a cyberattack.
To lower the risk of costly mistakes from happening, if not eliminate them, you must limit employee access to your organization’s critical data.
According to Varonis’s Global Data Risk Report, 17% of employees access all sensitive business data. So, if there’s any way that a small business can decrease access to these files, the more secure your business would become.
2. Always Have Protection Against Viruses, Spyware and Malware
All companies need to install security apps and antivirus software on all devices used for work. New threats are constantly arising and old threats are changing. It’s necessary to stay on top of the most recent updates from your antivirus company to protect yourself.
Hackers can access your computer network through outdated applications with known vulnerabilities. So, make sure your employees are aware of updating and patching software when they’re available.
3. Assess Your Business Risk
Another step to being more secure online is to fully understand the risks. Be aware of areas that need better protection. This includes your physical and digital infrastructure.
Many small businesses have good record keeping, but if you can’t remember the password to an administrator account for a backup system, it’s going to be hard to recover from a cyberattack.
4. Manage Your Passwords Better
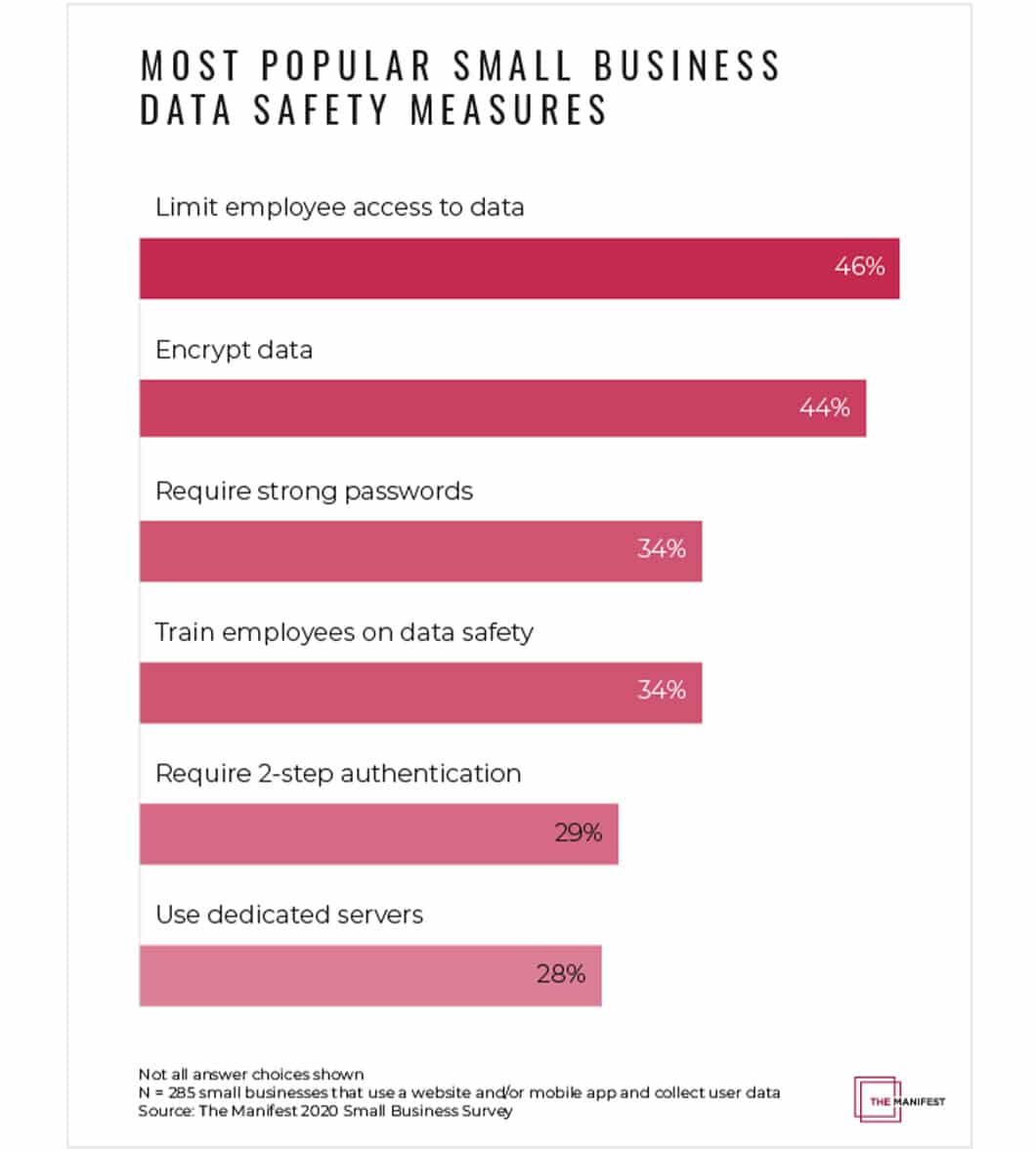
The Manifest’s Data Safety for Small Businesses lists requiring strong passwords as third among the most popular small business data safety measures.
Using strong passwords goes both ways. For employees, using a password-protection program is a great way to generate random passwords that are difficult to crack. Employees can then save the password in the program so they won’t forget. For business owners, setting up password-protected access to the internet connection prevents employees from simply logging on and off their network.
Only authorized personnel will be able to log in to these resources, allowing for a safer and secure network for your company.
5. Backup Your Data
Data loss can be a result of losing track of a physical server or hacking your peripheral systems. Make sure to backup data automatically in either an off-site location or on the cloud. That way you’re covered in case something happens.
6. Secure Your Network Using a Virtual Private Network
A virtual private network (VPN) encrypts all the traffic from and into your devices. If someone could get your information, they would only have encrypted data to retrieve.
This is vital if you have remote workers on your team. Because they’ll be working outside of the secure servers of your company, the VPN prevents users with unsecured networks from accessing your data.
Follow these small business cybersecurity tips and protect your operations.