For many business owners, pricing may feel like some sort of dark art. They look around, see what others are doing, pick a number and hope for the best.
But we know hope isn’t a good strategy when you’re running a company. How can you put yourself in the driver’s seat and make sure that your pricing strategy is designed to generate a sustainable profit?
The secret lies in the law of supply and demand, which will help you find that sweet spot at which your pricing strategy is optimizing demand and maximizing profits.
We’ll show you how to apply the theory to real-world situations so you can manipulate the law of supply and demand to your advantage.
Regarding the Law of Supply and Demand
The law of supply and demand illustrates the dynamic between the quantity of a good that’s made available in the market and the quantity that’s needed by the market in relation to pricing.
As a quick refresher, the law of demand states that buyers will want less of an economy good when the price increases and the law of supply says that sellers will supply more of a product when the price increases.
Market supply and demand are shaped by various factors that affect a seller’s ability to supply a product and a buyer’s willingness to purchase a good.
These 2 rules create a dynamic that determines the market price and volume of goods that are bought and sold. This relationship between supply and demand can be illustrated in the form of a supply and demand curve:
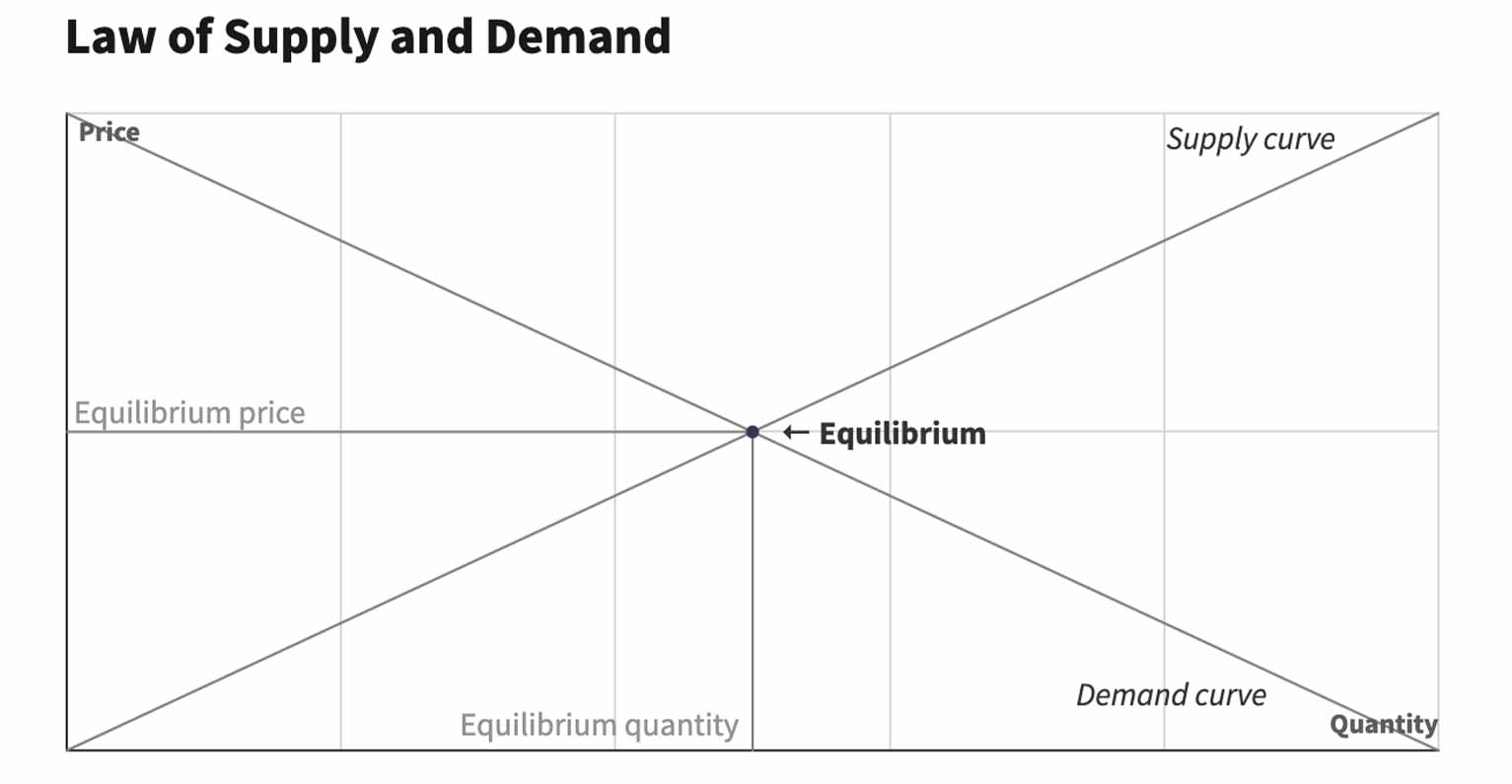
What Are the Four Basic Laws of Supply and Demand?
The basic laws of supply and demand illustrate how people’s willingness to buy or sell a good affects the price and quantity being traded. The prices and availability are adjusted until an equilibrium is reached.
- An increase in demand will lead to a higher equilibrium price and higher quantity if the supply remains the same.
- A decrease in demand will result in a lower equilibrium price and lower quantity if the supply is unchanged.
- An increase in supply will lead to a lower equilibrium price and higher quantity if the demand remains constant.
- A decrease in supply will result in a higher equilibrium price and lower quantity if the demand is unchanged.
Finding Your Sweet Spot: The Equilibrium Price
The equilibrium price is the price that the market will bear at a specific level of supply and demand. It’s the point at which the upward-sloping supply curve intersects with the downward-sloping demand curve.
At the equilibrium point, the price is high enough for suppliers to bring a specific quantity of goods to the market. It also is low enough such that consumers are willing to pay for the item. This creates a situation in which supply and demand are in balance.
To determine the exact price and quantity at which equilibrium occurs, we need to understand the factors that affect supply and demand.
Supply is predominantly a function of production costs such as labor and materials, the technology available to combine the inputs, the number of sellers and their production capacity as well as taxes, fees or other institutional regulations that may limit access to resources or the capacity of the production process.
Demand is mostly impacted by consumer preferences, as well as the availability and prices of other goods that can be used as substitutes. The change in the demand for a complementary good (which is used together with the product,) seasonal fluctuations and advertising can also impact how much the market desires a good. In addition, demand can be affected by the economic situation, such as changes in income.
Why a Supply-and-Demand Analysis Is Key for Businesses
The law of supply and demand can help you determine your pricing strategy and the quantity of goods you should produce or stock to maximize profits.
For example, if each item you sell creates $100 profit but only 1 person wants to buy it, you make $100. If you price it such that you only make $1 profit but 100 people buy it, you make $100. If you adjust the pricing so each item yields $50 profit and 50 people are buying it, you make $2,500!
By understanding what your customers want and how much they’re willing to pay for it, you can make informed decisions about what to offer and how to price it so you can generate the highest profit.
How to Apply the Law of Supply and Demand in Your Business
Before we show you how to effectively use the law of supply and demand to your advantage, let’s look at the main mistake made by most business owners.
The law of supply and demand states that a lower price leads to higher demand. However, adhering to such a price-led demand model means many business owners are lowering their prices just to get more buyers.
However, as you can see in the example above, selling 100 items that make only $1 profit is much less profitable than selling only 50 items but generating $50 of profit each.
Entering a price war is rarely a good idea for most businesses. Even if you can make some quick sales, you’d likely be diminishing your profit margins and tarnishing your brand image by making your products appear to be of low quality.
This is even more problematic if you’re a service provider because lowering your price to get more clients could mean that you have to work long hours and not getting paid nearly enough for your experience, knowledge and expertise.
The good news is that you can manipulate the law of supply and demand to work to your advantage so you can optimize your pricing strategy for maximum profits.
Here’s why:
How many people want a certain product and how much they’re willing to pay isn’t simply determined by the cost of producing the item, which often matters less than a slew of other factors that change consumers’ perception of how much the product is worth to them.
For instance, a product is considered valuable if it can solve the buyers’ pressing problems, elevate their status or make them feel good. The more consumers perceive that your product is valuable, relevant and useful to them, the more they’re willing to pay for it.
You can raise both the price and the demand for your product or service by making it more desirable to your customers.
Here’s how you can change the supply and demand curve to raise both the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity:
1. Position Your Products as a Rare Commodity
Consumers are willing to pay for what they perceive to be a rare commodity that only people with a certain status, resources or connections can access. For instance, limited edition items (e.g., handbags, sneakers) produced in small quantities and available only to an exclusive customer list can command a higher price than mass-produced goods, even if the production cost is the same.
Another example is diamonds, which are perceived to be rare only because of savvy marketing campaigns.
Take De Beers, for example. The diamond supplier creates an image of high value and exclusivity for the gem and limits the quantity available to keep the price high. After all, a piece of diamond sitting on a finger doesn’t have much (if any at all) utilitarian value. It fetches a high price simply because the buyers consider it to be desirable.

To create a sense of scarcity, set up limited-time access to or produce a limited quantity of a product. In addition, merchants can build anticipation by promoting a waitlist for upcoming launches, restaurants can limit seating and the number of patrons served per night, while service providers can have prospects go through a client selection process.
2. Limit the Supply of Your Products
The law of supply states that a decrease in supply will result in a higher equilibrium price if the demand remains constant. Therefore, if you limit the quantity of a good in the market, then you can increase the price, sell the same quantity and increase your profits.
But most products and services aren’t one-of-a-kind, which means the quantity supplied by other sellers isn’t under your control. How can you limit the supply? Here are a few things you can do:
- Control your schedule: If you tell prospects that your calendar is wide open, you create the impression that your time is in abundant supply and therefore, not valuable. Control your schedule and limit your availability by setting aside specific time slots for meeting with prospects, customers or clients.
- Define your niche: While you can’t limit what your competitors sell, you can redefine your market and narrow down your niche to make yourself the only one or one of the very few providers of a specific type of product or service.
- Create unique packages: Even if your products or services aren’t one of a kind, you can combine them in unique ways to make your offerings stand out. You can also establish a unique positioning by providing amazing customer service, a one-stop-shopping experience for a specific clientele or a return policy that exceeds expectations.
- Build a personal brand: Creating a unique personal brand that reflects your vision and unique approach within a niche market can help amplify the perception that your offering is one of a kind.

3. Create Demand for Your Products
People want to purchase from or do business with brands that are in demand. Remember the law of demand states that an increase in demand will result in a higher equilibrium price and a higher quantity sold if the supply remains the same? Therefore, you can increase profits by making more people want to buy your products.
Of course, you can sell something that’s already in demand, but you’d likely face intense competition. What if you can make more people want to buy what you want to sell? Here’s how to increase demand for your offerings:
- Pique curiosity: Generate excitement about a new product or service that you’re about to launch by dropping hints to your email subscribers, social media followers and existing customers.
- Build buzz and anticipation: Get your loyal customers, brand evangelists, journalists, influencers, bloggers, etc., to talk about your products or services and build anticipation around your launches.
- Control your message: Besides getting people to talk about your products, make sure the message is communicated correctly. You should make it easy for influencers and fans to share news about your brand so the right message will get to the right people.
- Orchestrate your launches: Not only do you need to build anticipation but you also have to control the timing so the buzz will keep increasing leading up to a product launch. You can drip out “sneak peeks” and keep evangelists engaged with new information.
- Implement a scalable strategy: To generate demand, you need to spread the word far and wide. As such, the tactics you use to build buzz should be scalable so it can grow with your brand.
4. Raise the Perceived Value of Your Offerings
Demand is led by value. If people perceive that they’re getting more value than what they pay for, the demand will increase even if you keep the price constant. Therefore, you can increase the demand for your products or services by making people feel that they’re getting a bargain without entering a price war.
Focus on what your clients or customers want — understand their needs and tailor your communications to show how your offerings solve their burning problems or help them create desired outcomes. Also, people are willing to pay more for an outstanding customer experience, which adds to the perceived value of your products or services.
You may need to segment your audience and create different marketing content based on what a specific clientele wants and how you can solve its challenges so you can highlight the values that you deliver.
When you create an intense demand for your products or services, you can move from demand-led pricing to value-led and quality-led pricing. This allows you to name your price while maintaining a high level of demand for your offerings.
The Law of Supply and Demand: The Key to Long-Term Profitability
Understanding the dynamic between supply and demand in your market is the key to finding the sweet spot — the equilibrium price — at which you can optimize the number of buyers at a specific price point to maximize your profits.
You can turn the dials by creating demand and adjusting supply so you can create a win-win situation in which your customers get what they want at the price they deem fair while you generate a sustainable profit for your business.